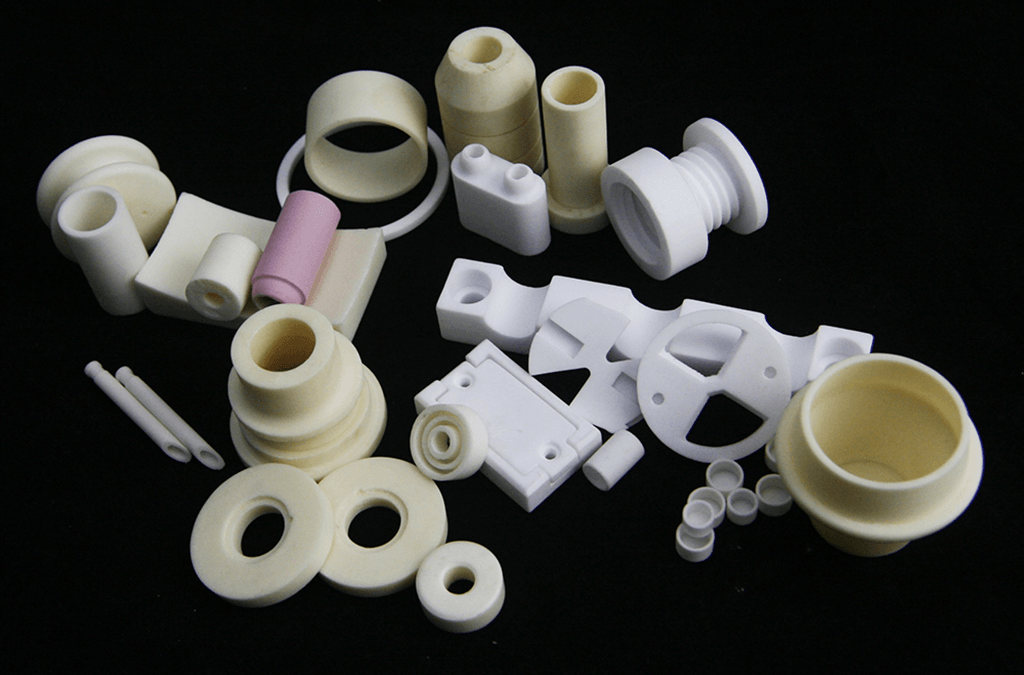
Ceramic injection molding technology, referred to as CIM, is an important branch of powder injection molding (PIM) technology. It is also developed on the basis of relatively mature polymer injection molding technology. Because it can produce products with complex shapes and has the advantages of high dimensional accuracy, smooth surface, and low cost, it has developed rapidly.
Overview of Ceramic Injection Process
Ceramics are broadly divided into daily ceramics and industrial ceramics. Here we mainly introduce industrial ceramics. There are many types of industrial ceramics, the commonly used ones are alumina, zirconia, silicon carbide, silicon nitride, boron nitride, etc. Industrial ceramics generally have high hardness, wear resistance and high temperature resistance, as well as high corrosion resistance, so they are widely used in electronics, machinery, chemical industry, aerospace and other industries.

There are generally three molding methods for industrial ceramics. The first is the casting method; the second is the dry pressing method; and the third is the injection method. Here we mainly introduce ceramic injection molding technology (Ceramic Injection Molding CIM). For different types of ceramics, the injection molding processes are similar, and are collectively referred to as ceramic injection below.
Ceramic injection molding is a method of preparing ceramic parts with complex shapes and excellent properties by mixing ceramic powder with organic binders, grinding, mixing, granulating, feeding, injection molding, degreasing and sintering. Molding technology. This technology has the advantages of high molding accuracy and high efficiency, so it has been widely used in the ceramic field.
The following is a detailed explanation of these processes:
▪ Powder grinding: Grind the original ceramic powder to improve its fluidity and uniformity, which is beneficial to the subsequent injection molding process.
▪ Internal mixing of ceramic powder and plastic binder: Mix the ground ceramic powder with an appropriate amount of binder, and prepare fluid ceramic injection raw materials through mixing, mixing, drying and other processes in an internal mixer. For injection molding, the adhesives include PP, PE, PA, POM, etc.
▪ Feeding injection: Inject the ceramic injection slurry into the mold, and through processes such as pressure holding, cooling and demoulding, ceramic parts with a certain shape and size are obtained.
▪ Degreasing: By heating or other physical and chemical methods, the adhesive is removed from the ceramic parts to obtain a green embryo with a basic shape.
▪ Sintering: The green embryo is sintered at high temperatures to densify it and form the final ceramic product.

Injection molding machine selection
The adhesive may be made of different raw materials, so when selecting the machine, especially the screw, the characteristics of the ceramic raw material and the adhesive must be taken into consideration.
▪ Screw and barrel selection: Although different types of ceramics have greatly different hardness and other properties after sintering, they are basically the same in the raw material stage before sintering. They are basically very similar to mud. Generally speaking, the proportion of binder It will not exceed 20%. These ceramic materials will cause a lot of wear on the screw barrel. When selecting screws, it is best to choose screws made of high-speed steel or other carbide materials and barrels with internal nickel-based alloy sleeves. The screw compression ratio is generally controlled between 2.0 and 2.3, the screw length-to-diameter ratio is about 22:1, the front end of the screw is equipped with an open mixing head, and the head flange needs to add a vent hole.
▪ Power selection: Unlike ordinary injection molding, there are degreasing and sintering processes after ceramic injection molding, especially sintering. If the internal stress of the injected ceramic green embryo is large, the deformation during sintering will also be relatively large. Therefore, choosing the appropriate power according to the wall thickness of the product is a key step. Generally speaking, we will choose the machine power to be larger than the actual power required in order to obtain a higher injection speed. As for the injection pressure, due to the poor fluidity of the ceramic slurry, a relatively large injection pressure is required.
▪ Selection of machine tonnage: The specific gravity of different ceramics varies greatly, so it would be more scientific for us to use the injection volume to select the type. Since ceramic injection does not require much clamping force, as long as the mold can be lowered and the injection volume is sufficient (the ratio of machine injection volume to product volume is best between 3:1 and 2:1), basic products can be produced.
▪ Selection of machine brands: There are not many mature machine brands for ceramic injection. Generally, brands such as Rigang, Arburg, Jibo and Haitian are mainly used.
Mold requirements
▪ Requirements for mold core steel: Also due to the abrasiveness of ceramics, the mold core material must also be made of alloy steel with higher hardness.
▪ Mold exhaust: Ceramic injection is used to prevent pores inside the product, which may lead to scrapping after sintering. Moreover, because adhesives often use POM and other raw materials that generate more gas, the exhaust requirements for the mold are relatively high. At the same time, since the injection speed cannot be too fast, the exhaust groove should be located as far as possible at the far end where the glue travels the slowest.
▪ Mold runner: Due to the poor fluidity of ceramic materials, it is generally not recommended to use hot runner, and the diameter of the cold runner should be as large as possible to facilitate the flow of ceramic raw materials.
▪Mold gate: As with the above two points, in order to increase the flow of ceramic raw materials and the need for exhaust, the mold gate generally needs to be larger.
▪The number of mold cavities: Since most ceramic products have certain size requirements, and since the ceramic green embryo still faces a sintering step after molding, the size of products with a large number of cavities is often difficult to control, so it is generally used A plan with a small number of holes.
Process adjustment
▪ Injection speed: In the ceramic injection process, too high an injection speed can easily produce defects such as pores and jet lines, while too slow a speed can lead to problems such as weld lines. Therefore, a process of slow filling through the gate and then medium-speed filling is generally used. .
▪ Injection pressure: Unlike ordinary plastic injection molding, excessive injection pressure may cause internal stress problems, which does not only refer to the holding pressure. Due to the poor fluidity of ceramics, large internal stresses will be generated at certain buckling positions during the injection process. The molded green embryo may not have any problems, but once it is sintered, these positions will produce larger internal stresses. Deformation, resulting in product scrap. Therefore, when injecting, try to use lower injection pressure. The same goes for holding pressure.
▪ Melt temperature: A higher material temperature is beneficial to eliminating product stress, but a too high material temperature will cause gas release and produce pores and other defects, especially for ceramic raw materials that use POM with a large amount of gas as a binder. .
▪ Mold temperature: Higher mold temperature is obviously beneficial to improving the fluidity of ceramic raw materials in the mold, thereby reducing the internal stress of the product. However, an excessively high mold temperature may cause the plastic used as a binder to float to the surface in contact with the mold core surface, which may affect the quality of the product after sintering.
▪ Mold opening speed: Since the physical properties of the newly formed ceramic green embryo are still relatively fragile, the mold opening speed should be relatively low and the vibration should be reduced as much as possible. The same goes for robot removal.
If you need industrial ceramic products, please feel free to contact me 0086-17702411651